|
|



Next: The exclusive mode
Up: The algorithm
Previous: The algorithm
The inclusive mode
The algorithm proceeds as follows:
- For every final state object1
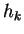 and for
every pair and for
every pair 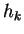 and and 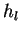 , compute the resolution variables , compute the resolution variables 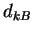 and
and 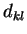 . The precise definition of these variables can be chosen
by the user (using the parameter angle), and will be
described in detail in section 2.4. They always have the
property that in the small angle limit they reduce respectively to the
squared relative transverse momentum of the object with respect to the
beam direction, and the squared relative transverse momentum of one
object with respect to the other. . The precise definition of these variables can be chosen
by the user (using the parameter angle), and will be
described in detail in section 2.4. They always have the
property that in the small angle limit they reduce respectively to the
squared relative transverse momentum of the object with respect to the
beam direction, and the squared relative transverse momentum of one
object with respect to the other.
At this stage, a dimensionless parameter 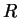 is
introduced[3], which plays a radius-like role in defining
the extent of the jets. This is usually set to 1.0. is
introduced[3], which plays a radius-like role in defining
the extent of the jets. This is usually set to 1.0.
- Scale the
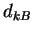 by by 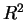
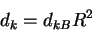 |
(3) |
- Find the smallest value among the
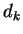 and and 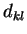 . If a . If a
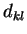 is the smallest, is the smallest, 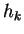 and and 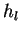 are combined into a single
object with momentum are combined into a single
object with momentum 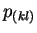 according to a user specified
recombination scheme (parameter recom) which will be
described in section 2.5. As an example, recom = 1 would
correspond to 4-vector addition. If a according to a user specified
recombination scheme (parameter recom) which will be
described in section 2.5. As an example, recom = 1 would
correspond to 4-vector addition. If a 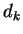 is the smallest, object is the smallest, object
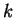 is defined to be a jet and is removed from the list of objects
to be merged. is defined to be a jet and is removed from the list of objects
to be merged.
- Repeat until all objects have been included in jets.



Next: The exclusive mode
Up: The algorithm
Previous: The algorithm
Jonathan Couchman
2002-10-02
|